The human frame is an intricately designed network of systems and organs, each with its own vital role in keeping health and capability. One of these systems, the circulatory gadget, consists of a huge network of blood vessels chargeable for transporting oxygen and vitamins to cells whilst eliminating waste merchandise. While this gadget encounters issues, it can cause diverse health troubles, and one such circumstance that often goes undetected until it becomes a considerable problem is Peripheral Vascular disease (PVD).
What's Peripheral Vascular Disease?
Peripheral Vascular ailment, also referred to as PVD or peripheral artery ailment (PAD), is a circumstance that impacts the blood vessels outside the heart and brain, usually concentrated on the arteries and veins within the extremities, most generally the legs. This ailment entails the narrowing or blockage of blood vessels, restricting the everyday drift of blood to the affected regions. when left untreated, PVD can result in excessive complications, affecting a person's basic fitness and mobility.
The Silent Progression of PVD
One of the most challenging aspects of PVD is that it often progresses silently. In its early stages, individuals may experience few or no symptoms, leading them to overlook the condition until it becomes more advanced. This delayed awareness can have serious consequences for their health and quality of life.
Common Risk Factors
Several risk factors contribute to the development of PVD. These include:
Smoking: Smoking is a main hazard element for PVD. The dangerous chemicals in tobacco can damage blood vessels and increase the threat of plaque buildup.
Diabetes: People with diabetes are at a higher hazard of growing PVD due to elevated blood sugar tiers that can damage blood vessels.
High blood pressure: High blood pressure can strain and damage arteries, making them more vulnerable to narrowing.
Excessive LDL cholesterol: Elevated cholesterol levels can lead to the buildup of fatty deposits in blood vessels, inflicting blockages.
family records: A circle of relatives' history of vascular illnesses can increase a man or woman's threat of growing PVD.
Age: PVD becomes more commonplace as humans age, with those over 50 being a better threat.
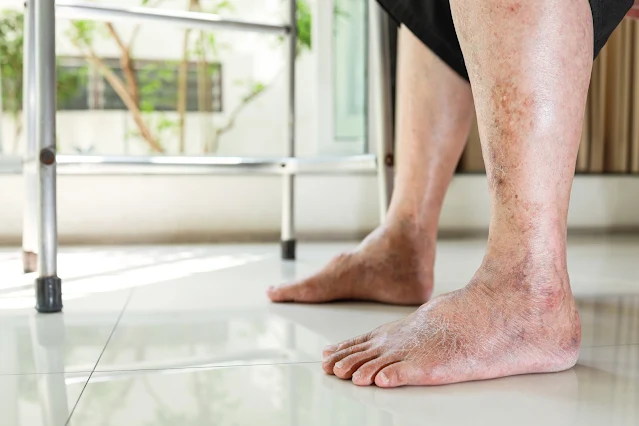
Symptoms of Peripheral Vascular Disease
As PVD progresses, individuals may experience various symptoms, including:
Claudication: This is a common symptom of PVD, characterized by pain, cramping, or fatigue in the legs during physical activity.
Numbness or Weakness: Reduced blood flow can cause numbness or weakness in the affected limbs.
Cool Skin: The affected area may feel cooler than the surrounding skin due to decreased blood circulation.
Slow Wound Healing: Wounds, particularly in the legs or feet, may take longer to heal.
Skin Changes: Skin color changes, such as pallor or blueness, can occur.
The Importance of Early Diagnosis and Intervention
Early diagnosis of PVD is crucial for several reasons:
Preventing Complications: Timely intervention can prevent complications such as ulcers, gangrene, and limb amputation.
improving quality of existence: Handling PVD in its early stages can alleviate signs and enhance a man or woman's universal fine of life.
Lowering cardiovascular hazard: PVD is related to a multiplied threat of heart assaults and strokes. Treating PVD can reduce this risk.
Lower Healthcare Costs: Early detection and management of PVD can result in lower healthcare costs compared to treating advanced stages of the disease.
Expertise Peripheral Vascular ailment
Peripheral Vascular disease, often abbreviated as PVD, is a broad term encompassing a set of problems that affect the blood vessels of doors the heart and mind. The condition commonly targets the arteries and veins that supply the limbs—commonly the legs—and it outcomes from the narrowing or blockage of these blood vessels. Such obstructions limit the everyday float of blood, which could have severe results for the affected man or woman's fitness and mobility
The Silent Progression of PVD
One of the hardest components of PVD is that it regularly progresses silently, with diffused or even absent signs in its early degrees. this means that individuals might not recognize they have got a problem until the disorder has advanced substantially, making early analysis all the more critical.
common chance elements for PVD consist of smoking, diabetes, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and a family history of vascular diseases. However, even people without these chance factors can develop the condition, emphasizing the significance of regular take a look at-us and early detection.
The Importance of Early Diagnosis
Prevention of complications: Early prognosis lets in for well-timed intervention, that can prevent or put off the progression of the ailment. Left untreated, PVD can result in extra intense headaches, together with ulcers, gangrene, or even limb amputation.
progress satisfactory of existence: Handling PVD in its early levels can extensively enhance a man or woman's best lifestyle. signs and symptoms consisting of leg pain, cramping, and numbness may be alleviated with appropriate treatment and lifestyle modifications.
Lower Healthcare Costs: Detecting and addressing PVD early can result in lower healthcare costs in the long run. Advanced stages of the disease often require more intensive and costly interventions, such as surgeries and hospitalizations.
Reduced Mortality Risk: PVD is not just about limb health; it's also a marker for cardiovascular disease. Individuals with PVD are at an increased risk of heart attacks and strokes. Early diagnosis can lead to interventions that reduce this risk.
Methods of Diagnosis
Healthcare professionals use a variety of methods to diagnose PVD:
physical exam: A radical physical exam can monitor symptoms of decreased blood waft, inclusive of susceptible or absent pulses, cool pores, and skin, or wounds that can be gradually healed.
Ankle-Brachial Index (ABI): ABI is a simple and non-invasive take a look at that compares the blood strain on your ankle to that during your arm A lower ABI may indicate PVD.
Ultrasound: Doppler ultrasound imaging can visualize blood flow in the affected arteries and detect blockages or narrowing.
Angiography: In more complex cases, angiography, which involves injecting a contrast dye and taking X-rays, may be necessary to pinpoint the exact location and extent of arterial blockages.
Interventions and Treatment
Early intervention can take diverse forms, depending on the severity of the ailment. lifestyle modifications, together with smoking cessation, regular exercise, and a coronary heart-wolesome eating regimen, are often the first steps. medicinal drugs to manage risk elements like excessive blood stress and excessive cholesterol will also be prescribed.
For more superior instances, minimally invasive procedures like angioplasty and stent placement may be used to reopen blocked arteries. In extreme cases, surgical bypass procedures may be necessary.
Conclusion:
Peripheral Vascular Disease is a common yet
often overlooked condition that affects the circulatory system, primarily in
the legs. Recognizing the risk factors, understanding the symptoms, and seeking
early diagnosis and intervention are crucial for effectively managing PVD,
preventing complications, and maintaining a high quality of life. If you or
someone you know has risk factors for PVD or experiences related symptoms, it's
essential to consult a healthcare professional promptly to address this silent
threat to vascular health.










0 Comments